5G-EPICENTRE: AR-assisted emergency surgical care
ORamaVR leads the Use Case (UC) ”AR-assisted emergency surgical care”, identified in the context of the 5G-EPICENTRE EU-funded project. Specifically, the UC will experiment with holographic AR technology for emergency medical surgery teams, by overlaying deformable medical models directly on top of the patient body parts, effectively enabling surgeons to see inside (visualising bones, blood vessels, etc.) and perform surgical actions following step-by-step instructions (see Figure 1).

The PPDR responder uses an AR HMD to see overlayed info and deformable objects on top of the patient. Envisioned example of UI layout.
The goal is to combine the computational and data-intensive nature of AR and Computer Vision algorithms with upcoming 5G network architectures deployed for edge computing to satisfy real-time interaction requirements and provide an efficient and powerful platform for the pervasive promotion of such applications. Toward this end, the authors have adapted the psychomotor Virtual Reality (VR) surgical training solution, namely MAGES [4,5], developed by the ORamaVR company. By developing the necessary Virtual Network Functions (VNFs) to manage data-intensive services (e.g., prerendering, caching, compression) and by exploiting available network resources and Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) support, provided by the 5G-EPICENTRE infrastructure, this UC aims to provide powerful AR-based tools, usable on-site, to first-aid responders (see Figure 2 for an overview of the UC NetApps layout).
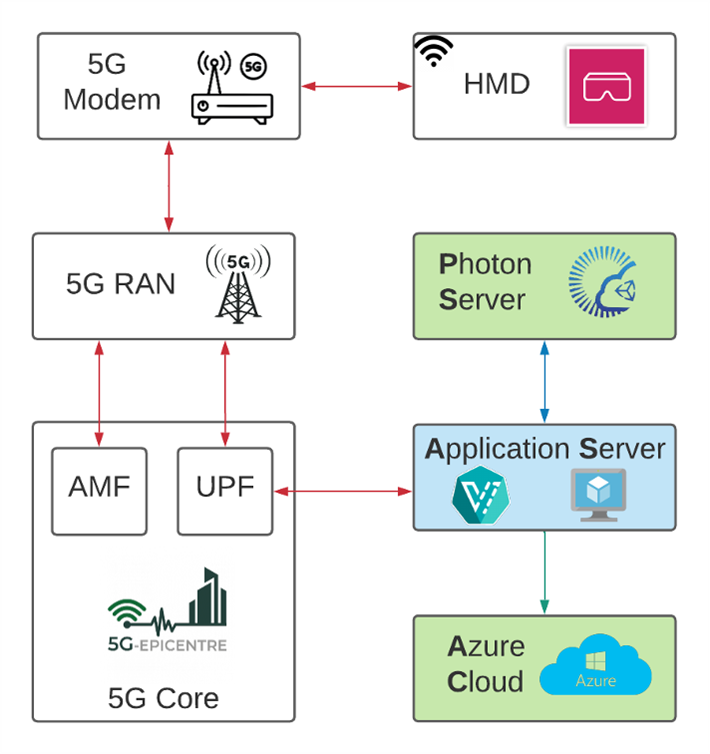
Envisioned layout of the UC components. Blue and Green nodes correspond to edge and cloud resources respectively.




